A beautiful Friday morning here in New York’s Finger Lakes…here’s the good news from this week.
First, the Supreme Court rejected the Purdue Pharma opioid settlement agreement – thereby allowing victims to pursue legal action against the Sackler family. As one who’s been deeply involved in the opioid disaster for a decade and half, I have somewhat mixed feelings about this – but have to support the Court’s decision.
The settlement would have shielded the Sackler family – many of whom were top execs and owners of Purdue – from personal liability.
It’s not hyperbole to say the Sacklers were directly responsible for the deaths of tens of thousands of daughters, sons, moms and dads, husbands and wives, friends and neighbors. The settlement would have allowed these killers to keep some of their billions while avoiding any potential criminal or civil liability.
The downside is the settlement would have provided hundreds of millions of dollars for treatment and recovery services for addicts…losing those dollars is a tragedy.
That said, its very likely the Sacklers and Purdue will still have to provide funds to victims…and some of the Sacklers will now face civil – and potentially criminal – prosecution.
Lower drug costs
From CNBC:
- The Biden administration will impose inflation penalties on 64 prescription drugs, lowering costs for certain older Americans enrolled in Medicare.
- A provision of Biden’s Inflation Reduction Act requires drugmakers to pay rebates to Medicare if they hike the price of a medication faster than the rate of inflation.
Lastly…
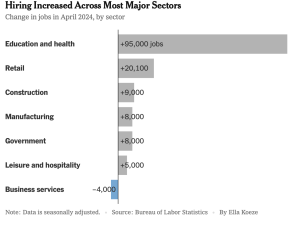
The economy grew by 3.1% YoY last year…a really solid result!

What does this mean for you?
Sacklers don’t avoid prosecution and liability, drug costs will drop, and the economy is pretty darn solid.