Today we’re doing a very quick recap of stuff we learned over the last couple of weeks…no opinion here (yeah that was really hard for me…)

Extra credit for identifying the man in the picture…
But first, for those of us perennially mad at ourselves because, well, we screw up and aren’t perfect, read this. Short take – perfectionism…
“…makes for a thin life, lived for what it isn’t rather than what it is. If you’re forever trying to make your life what you want it to be, you’re not really living the life you have.”
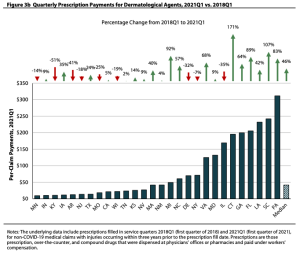
Drug prices
Make for great politics…even when all the caterwauling is wrong. The issue is what we – the consumer – pay is NOT what insurers, PBMs, and other payers pay.
That’s due to the “gross-to-net bubble”, a term popularized by the estimable Adam Fein Ph.D.
When rebates and discounts were factored in, brand-name drug prices declined—or grew slowly—in 2021.
So…you getting those rebate checks?
COVID’s origins
Remember the theory that COVID came from a Chinese lab? It is looking increasingly sketchy.
A comprehensive, detailed, and multi-factor analysis by scientists from four continents found
the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 occurred via the live wildlife trade in China, and show that the Huanan market was the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The peer-reviewed research published in the journal Science covered molecular epidemiology and spatial and environmental analyses.
Investors and physician practices
Private equity investment in physician practices varies a lot by specialty and region. Quick takes…
- about 5% of physicians were in private equity-acquired practices
- The highest percentage was in D.C. (18.2%)
- More than one in ten docs in AZ, CT, FL, MD, and FL were in PE-acquired practices
The researchers wrote…
“Because some private equity acquisitions consolidate physician practices into larger organizations, geographic concentration of private equity penetration may be associated with reduced physician competition, which could lead to increased prices, [emphasis added]
An interactive map and the research report are here.
Gun violence
Gun makers earned over 1 Billion (with a B) dollars from sales of military-style assault weapons over the last decade. A report to Congress found:
- gun makers marketed to young men by claiming their weapons will put them “at the top of the testosterone food chain”…
- the weapons were described as an “apex predator”
- some ads for these weapons “mimic first-person shooter video games popular with children.”
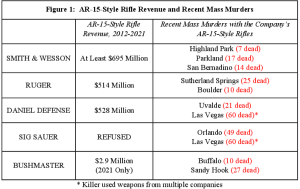
source here
The AR-15 is the most common of these weapons…the NRA named it “American’s Rifle” back in 2016. (and here I always thought it was Davy Crockett’s flintlock rifle…)
(disclosure – I hunt and have several rifles – none are semi-auto like the AR-15)
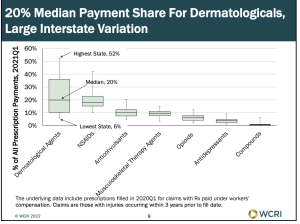
Workers’ comp physician fee schedules
…are all over the place…Louise Esola at Business Insurance reported on a recent WCRI analysis that found:
About one-quarter of the fee schedule states established their rates for office visits near the Medicare level or below, while about the same number of states set their fees for major surgery at triple the Medicare rates or more in each state…
The study – authored by Olesya Fomenko and Te-Chun Liu and up to date as of this spring – is here. (sorry for misspelling of Dr Fomenko’s name in earlier version…darn spellcheck!)
Clearly politics trumps policy…unless someone can tell us why it makes sense for Florida to pay docs below Medicare, while paying hospitals many times Medicare… I’ll stick to politics, campaign contributions, lazy legislators and hand-cuffed or ineffective regulators as the main driver of work comp fee schedules. (oops opinion inserted into post…just can’t stop myself)
Happy August!